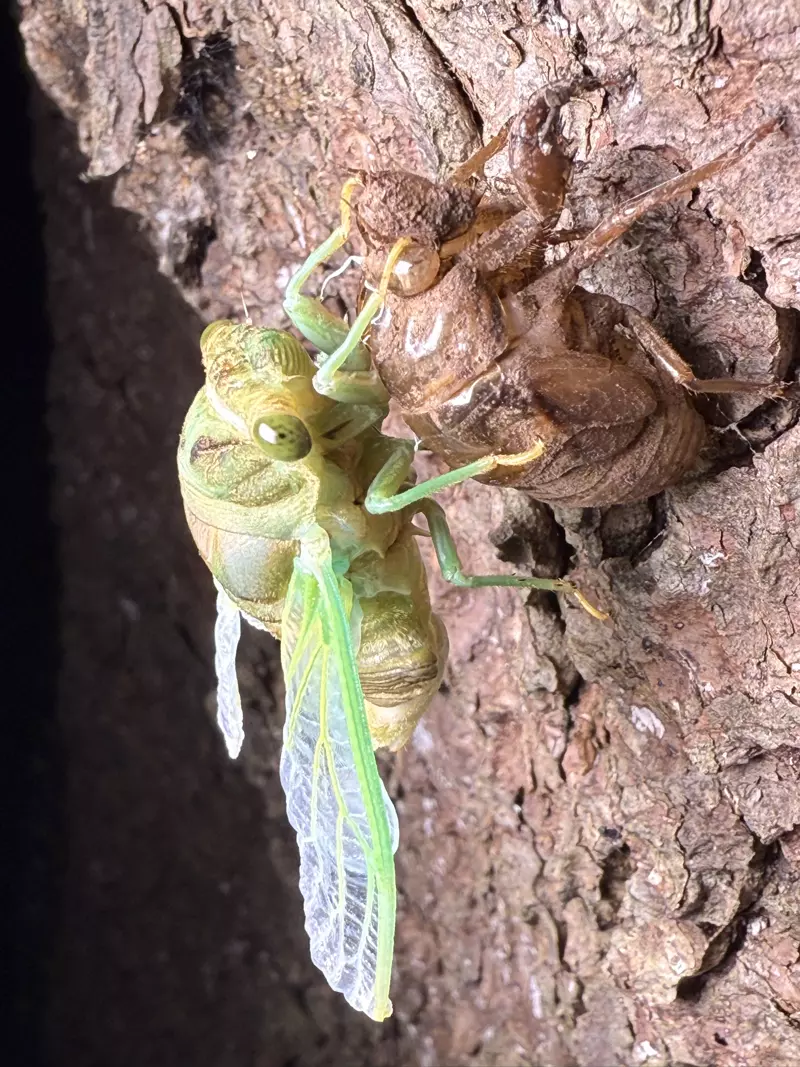
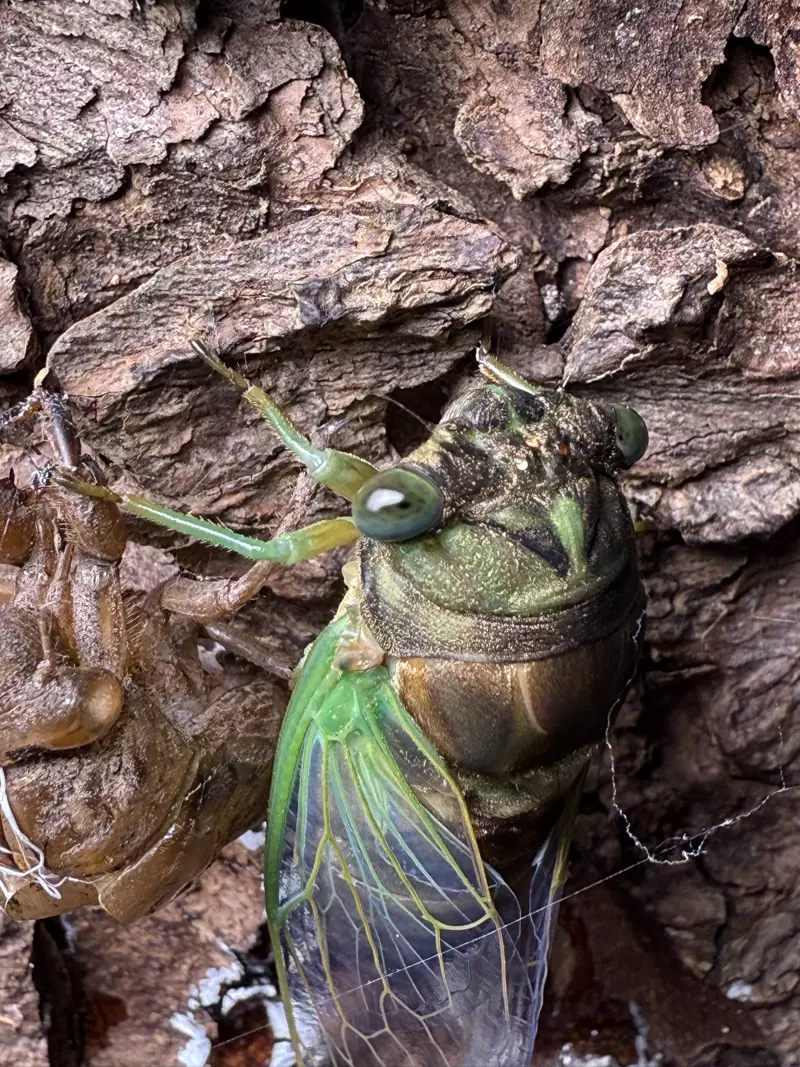
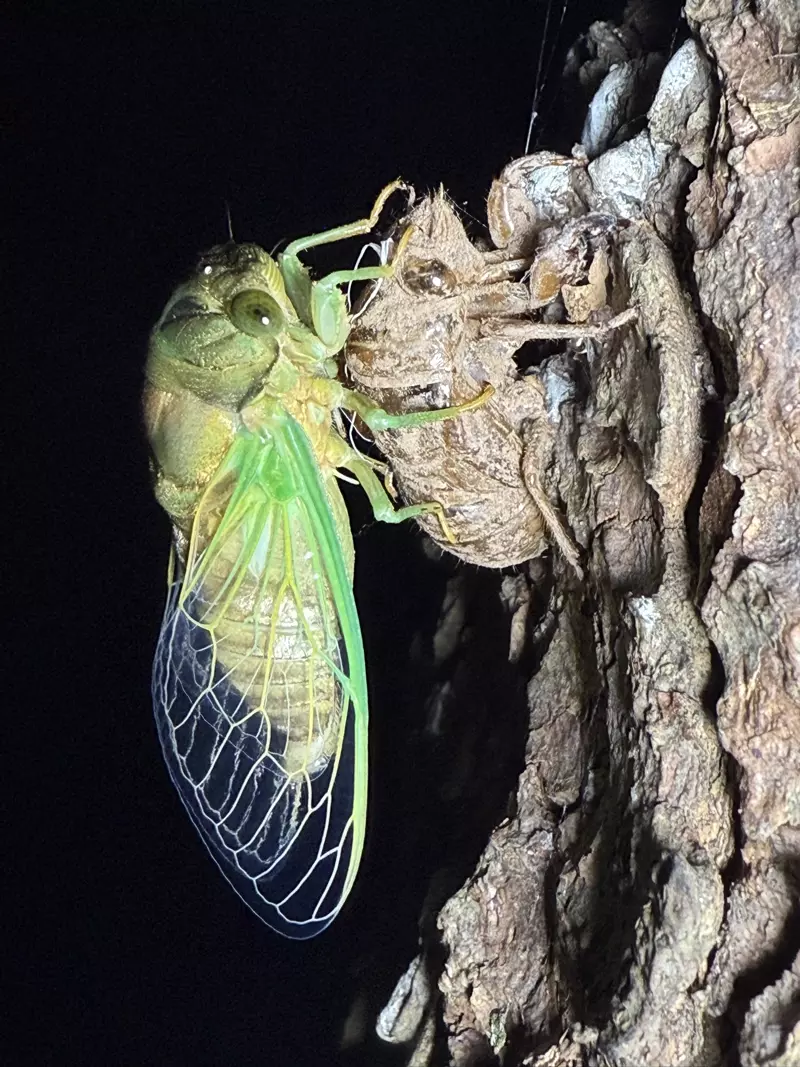
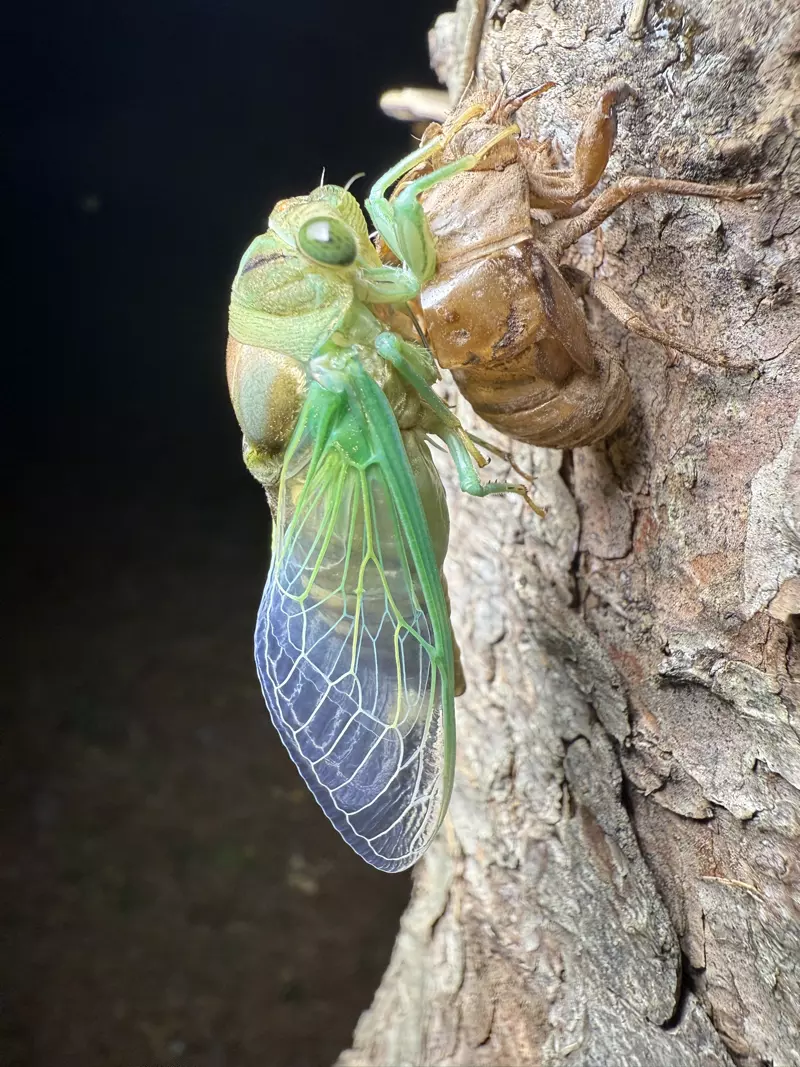
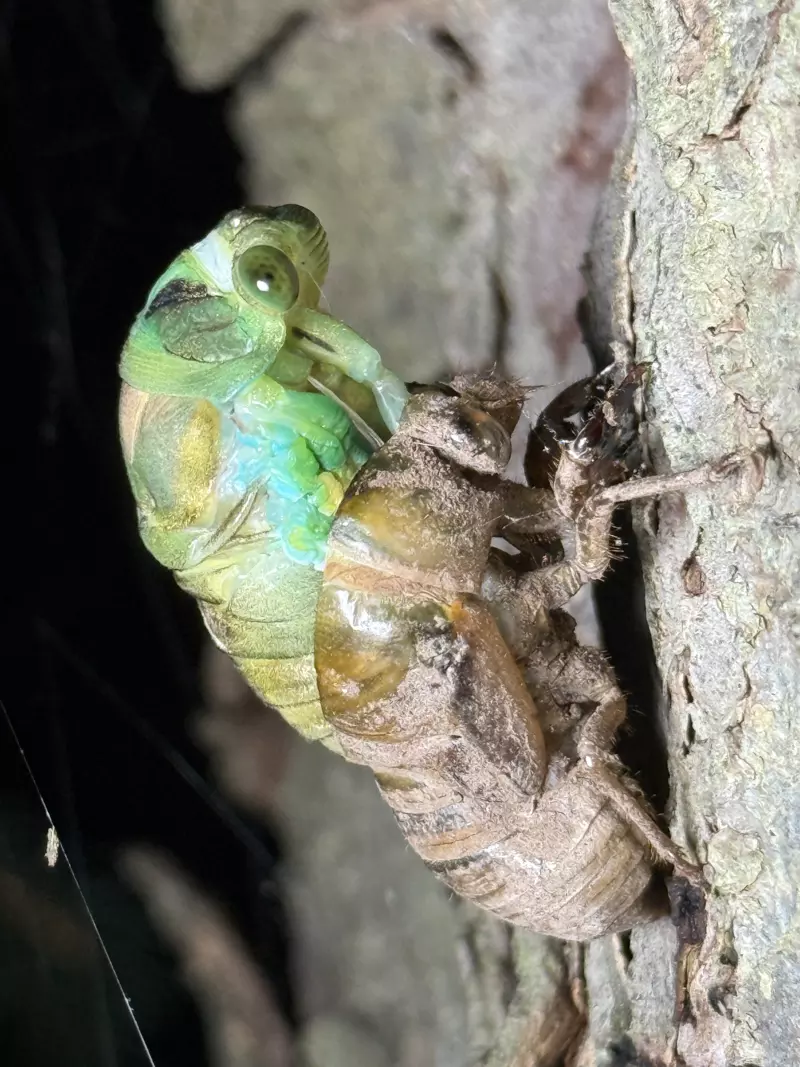
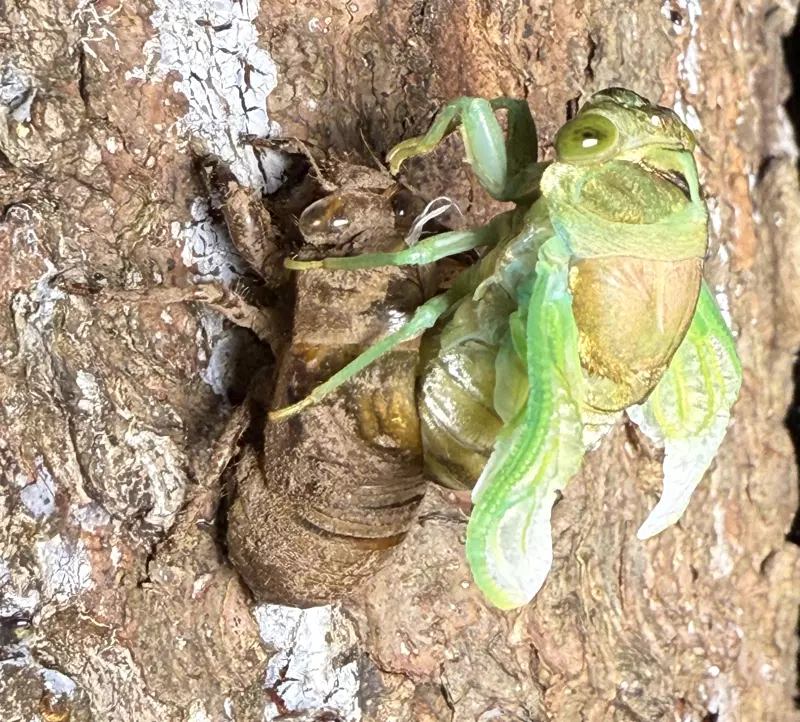
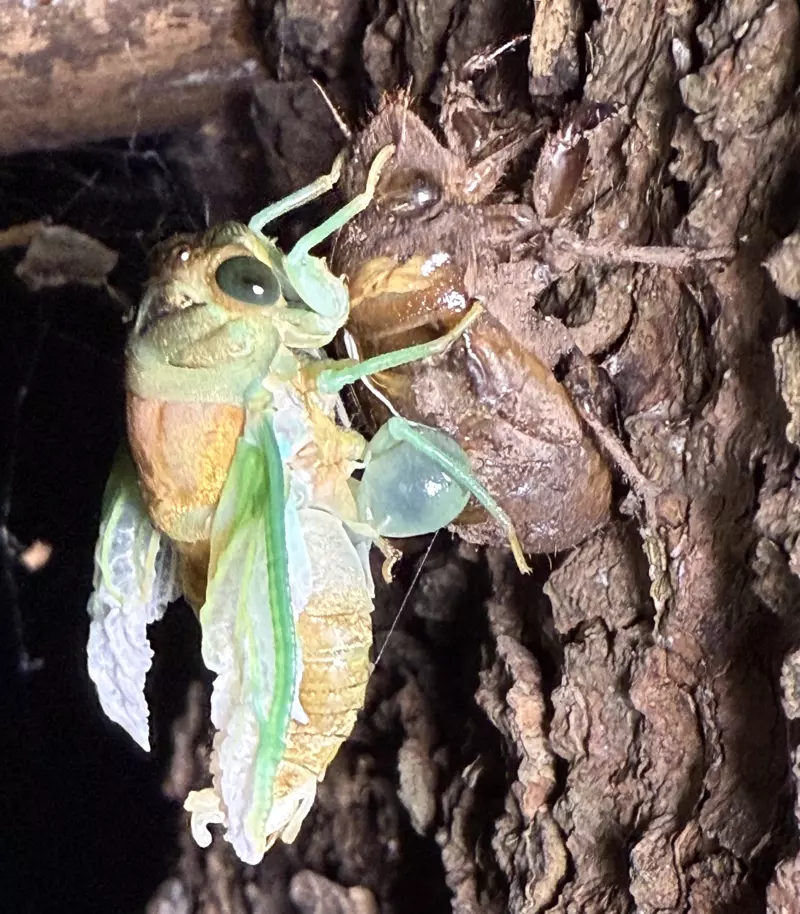
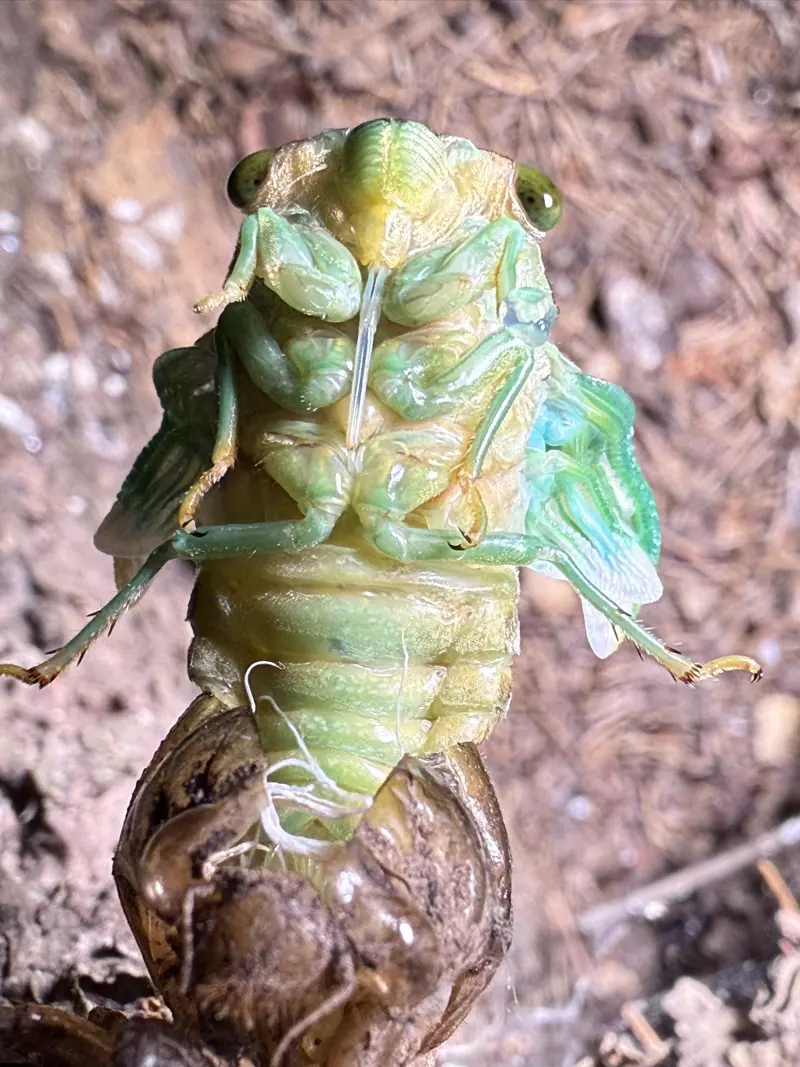
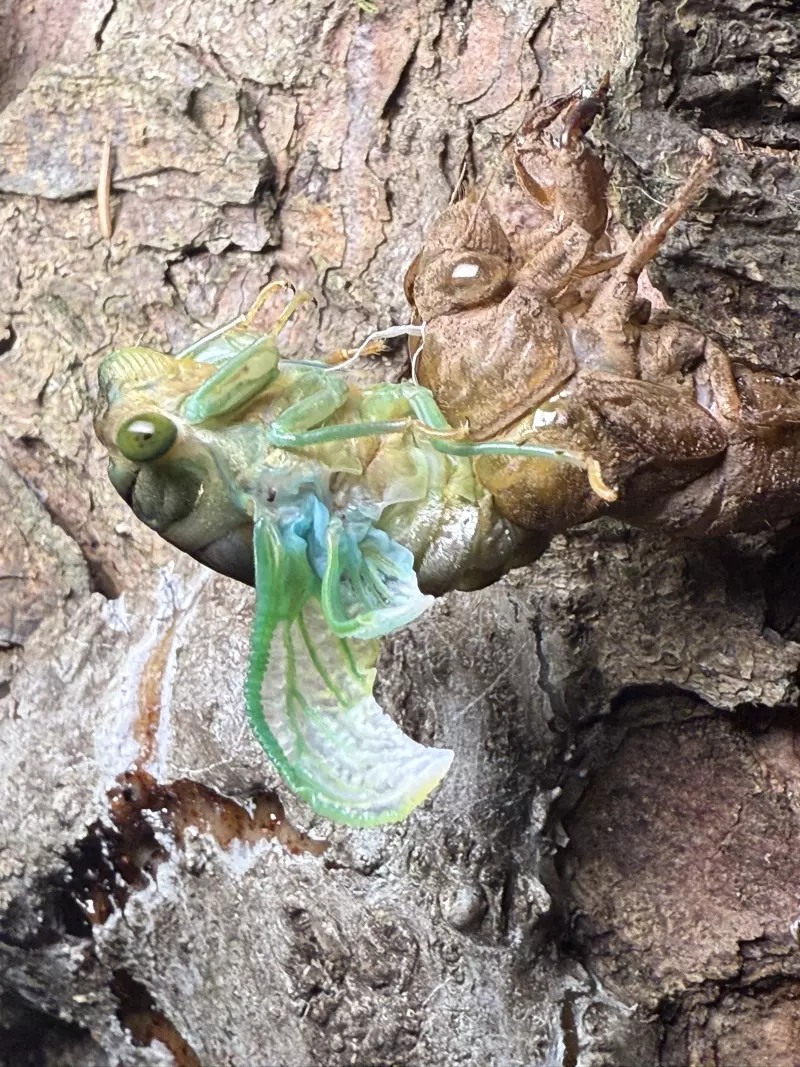
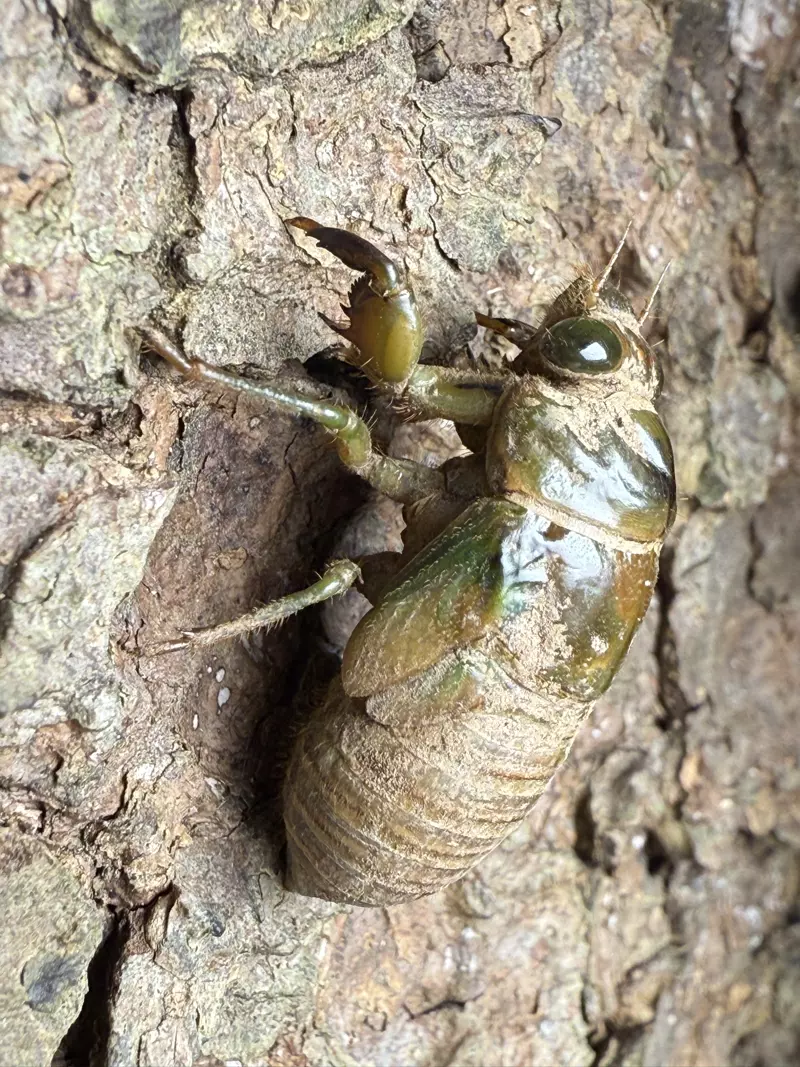
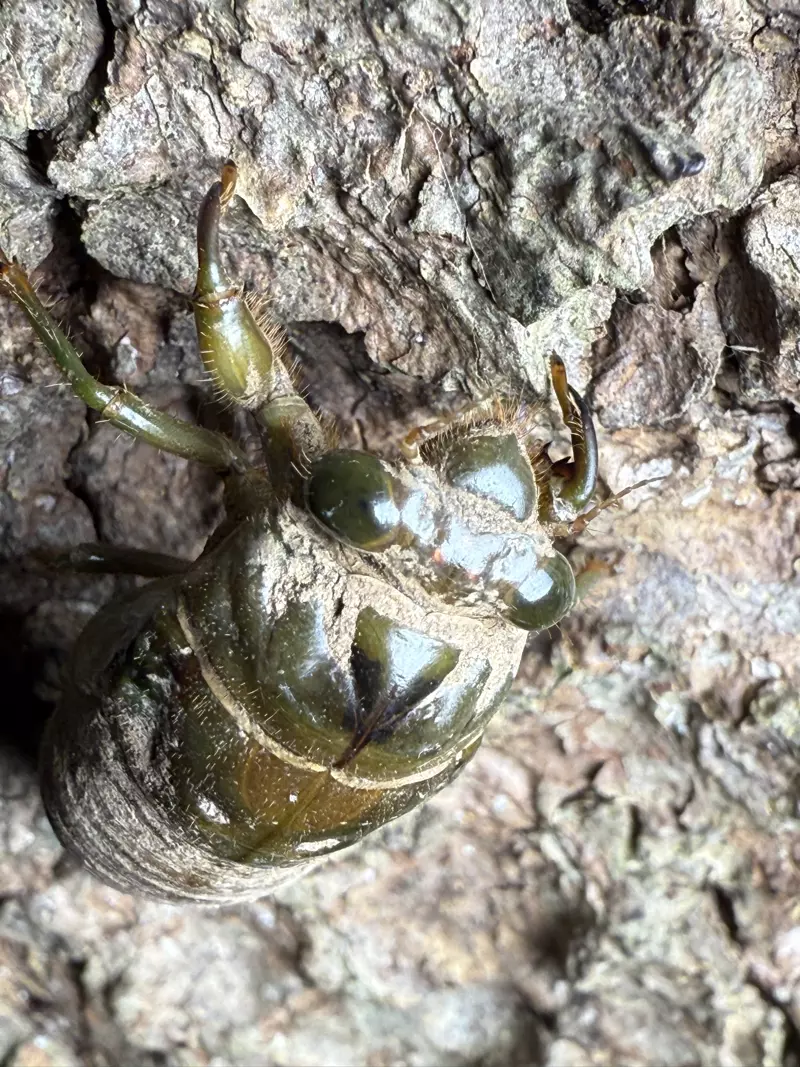
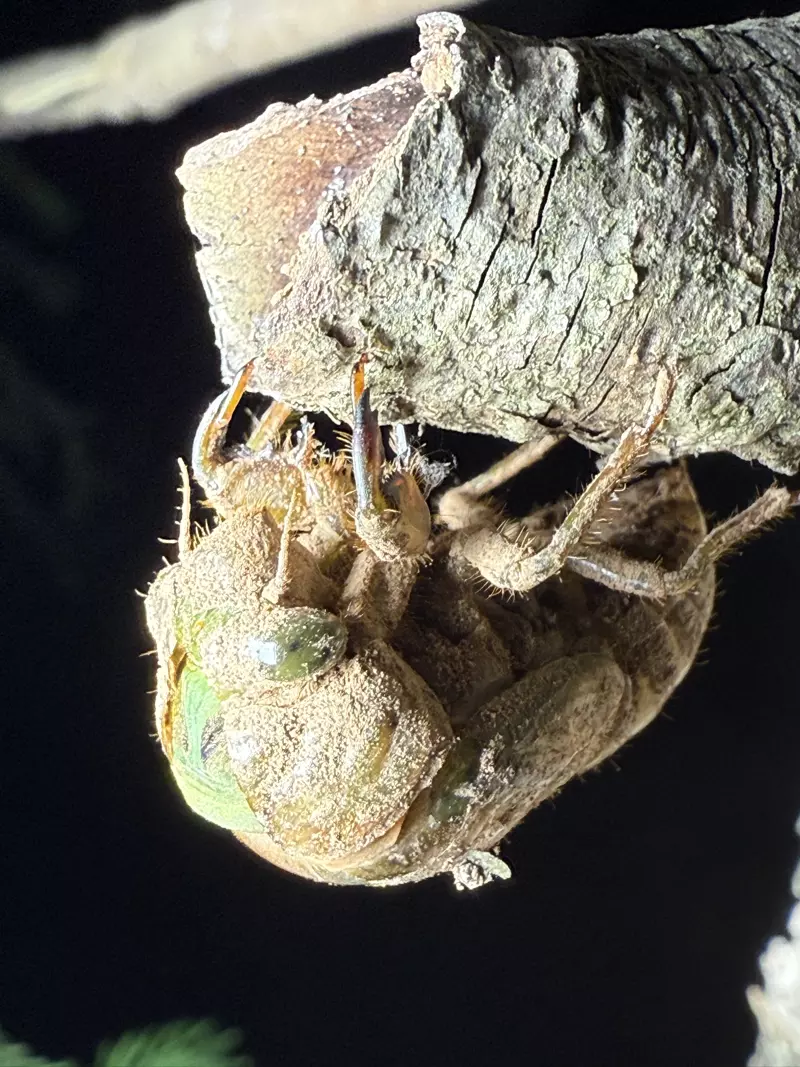
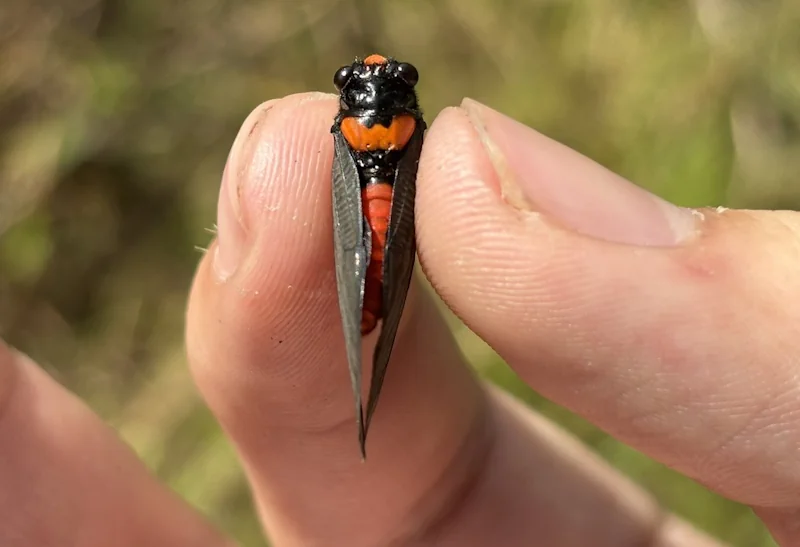
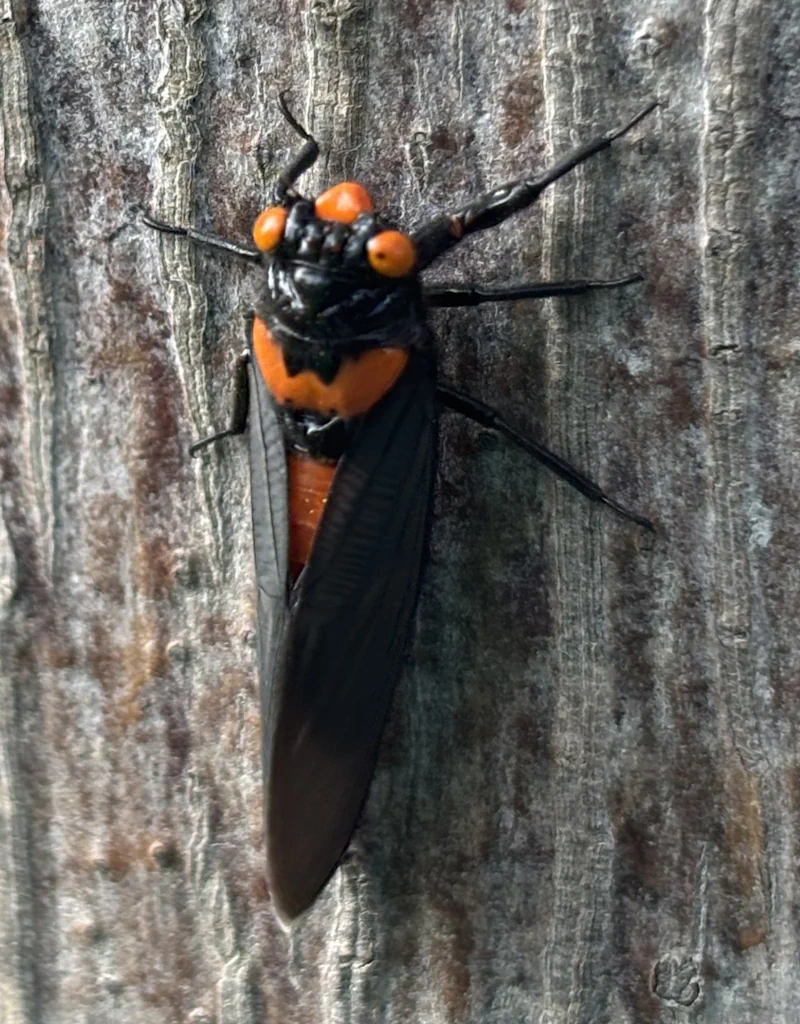
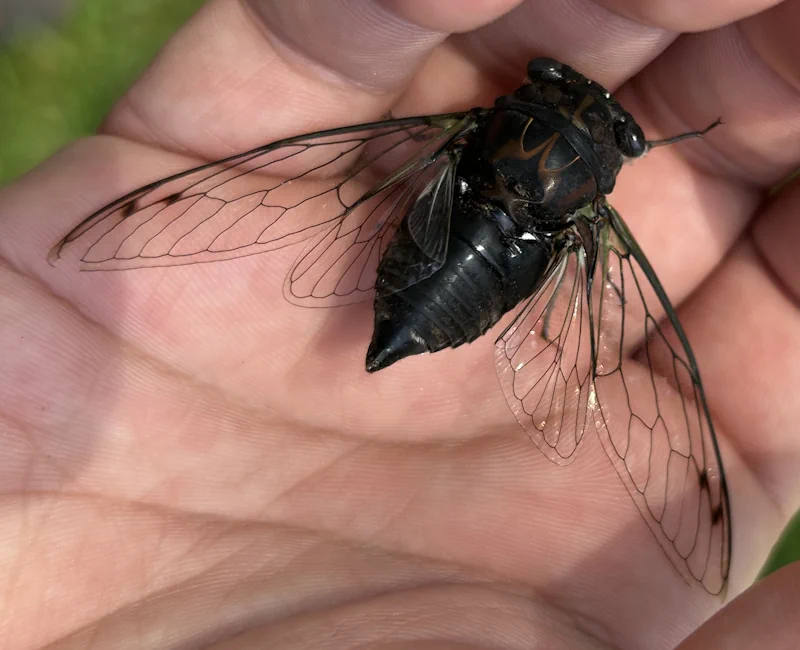
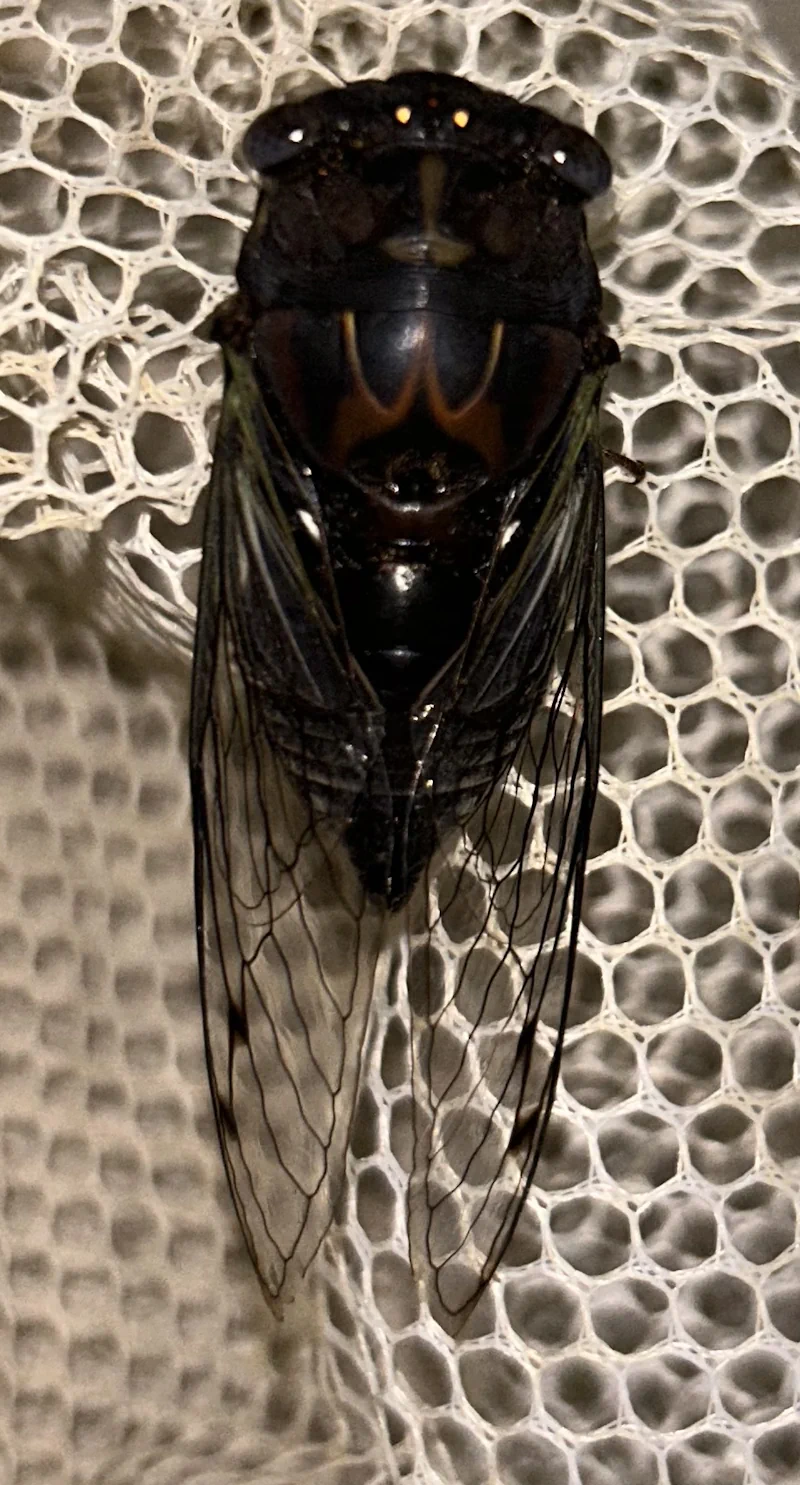
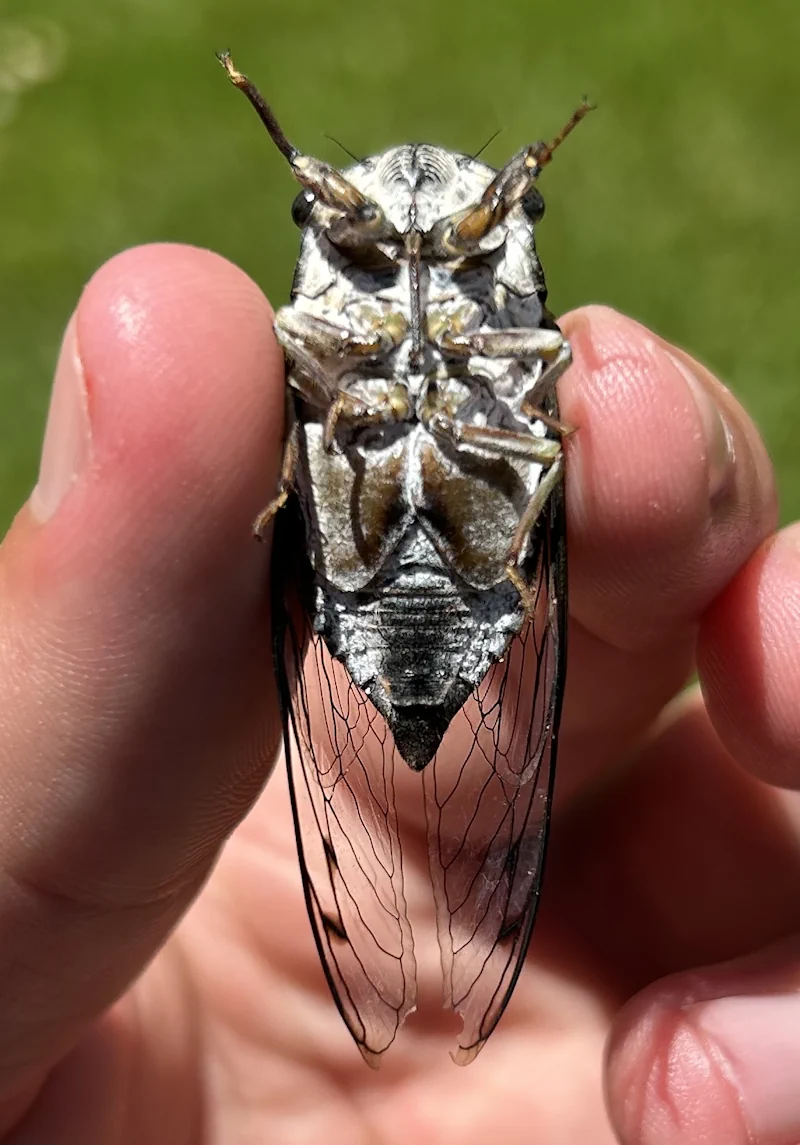
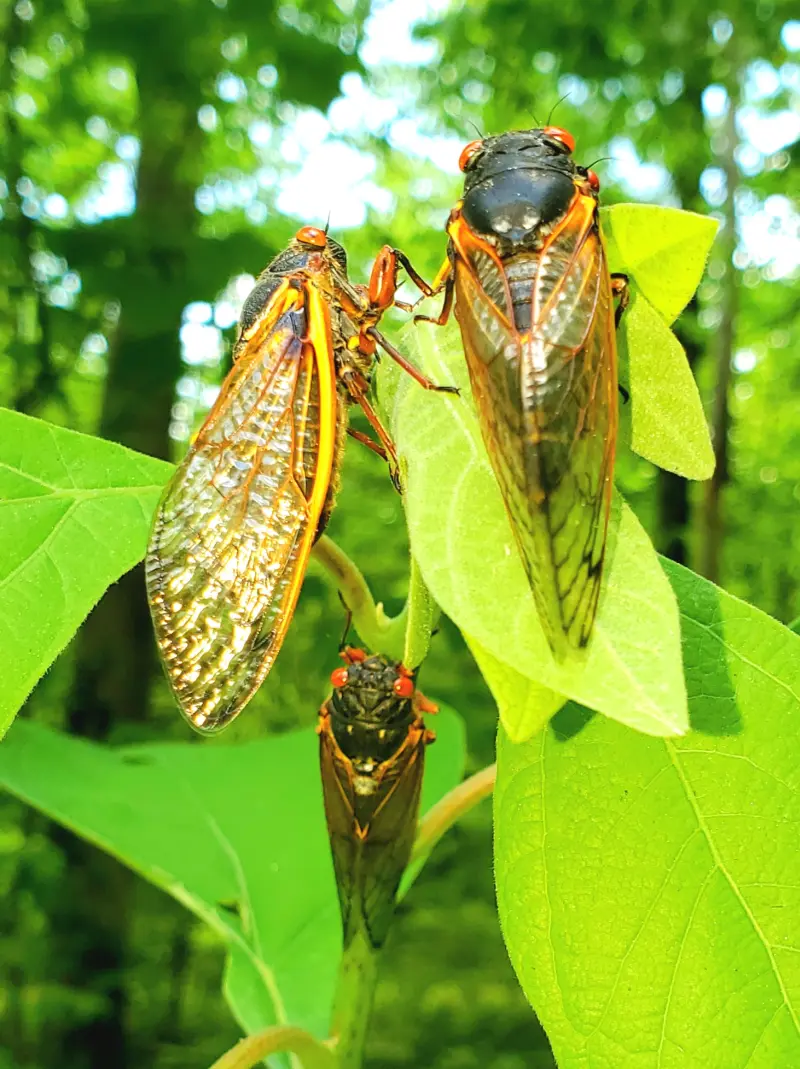
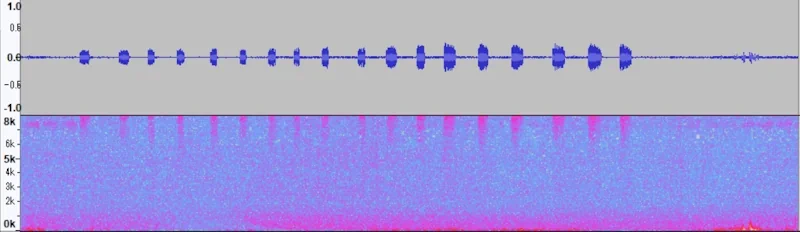
Magicicada periodical cicadas often emerge earlier or later than expected. This phenomenon is called straggling, and the individual cicadas that emerged earlier or later are called stragglers. Magicicada are presumed to straggle for a number of reasons including subterranean overcrowding and the effects of urban heat islands on subterranean environments (a recent phenomenon). Evolutionarily speaking, it is a mechanism that allows them to break away from their original brood and form a new one. Right now on the homepage of the UCONN Cicada site they have a good story about how Brood XIV connects to Brood X, which connects to VI, which connects to II.
Stragglers, in the past, were observed and documented (MORRIS,J. G. 1870. Seventeen-year locust two years too late. Amer. Ent., 2: 304.) but it is much easier to do so today thanks to apps like iNaturalist, Cicada Safari, and mobile phones and social media in general.
So, where are we observing stragglers in 2025?
Down in the Baton Rouge area of Louisiana, Brood XXII is emerging 2 years early (iNaturalist Map). Brood XXII typically has a 13-year lifecycle.

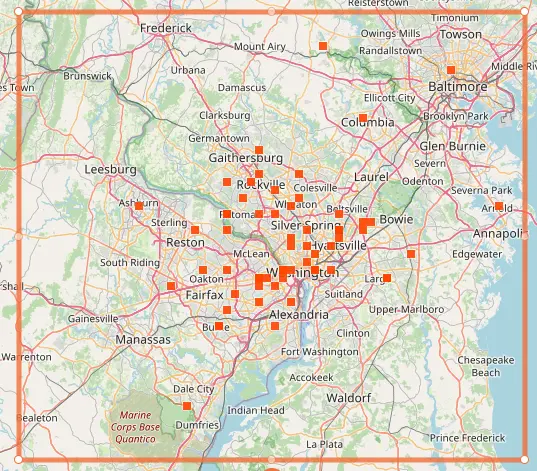
There are many Brood X stragglers emerging in the Washington D.C. area (iNaturalist Map).
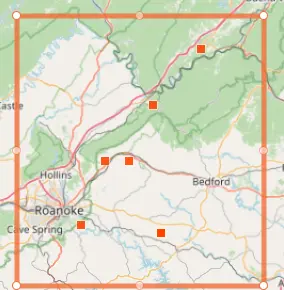
Brood I stragglers are appearing in the Roanoke, Virginia area emerging four years early. (iNaturalist map).
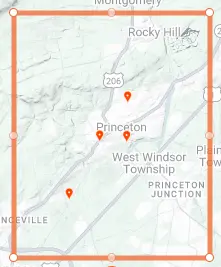
There are a handful of Brood X stragglers in the Princeton, NJ area. (iNaturalist Map).
And there are definitely more…
If you want to look for stragglers, online, you can use iNaturalist or the Cicada Safari app. Here is a map with all the Cicada Safari sightings on it.
And here’s a map that plots all the Broods, courtesy of Cicadas @ UCONN:
Two notes:
1) The general public does not like the term stragglers when applied to cicadas that emerge early, because straggling generally means to be late, not early. Marlatt referred to them as precursors (Marlatt, 1989). You can use that term if you like.
2) People called cicadas locusts in the recent past. Scientifically speaking and in modern times, a locust is a grasshopper. Cicadas and grasshoppers are very different insects, but they can emerge in large numbers and do some damage to plants (cicadas cause flagging on trees, while locusts eat everything), hence the confusion.