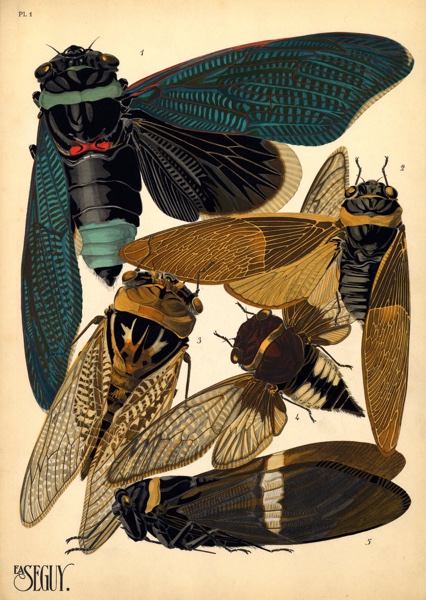
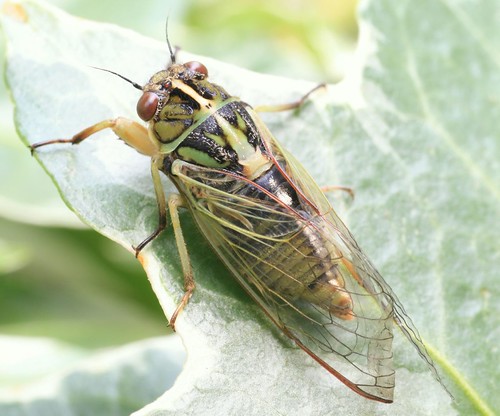
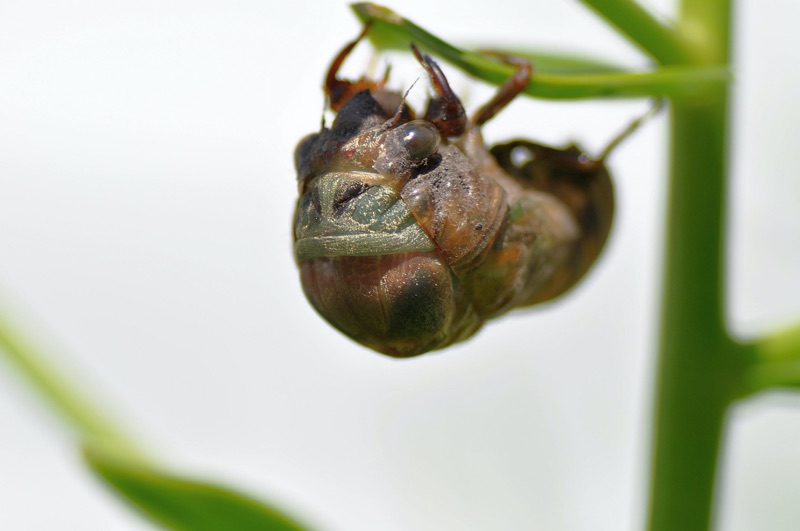
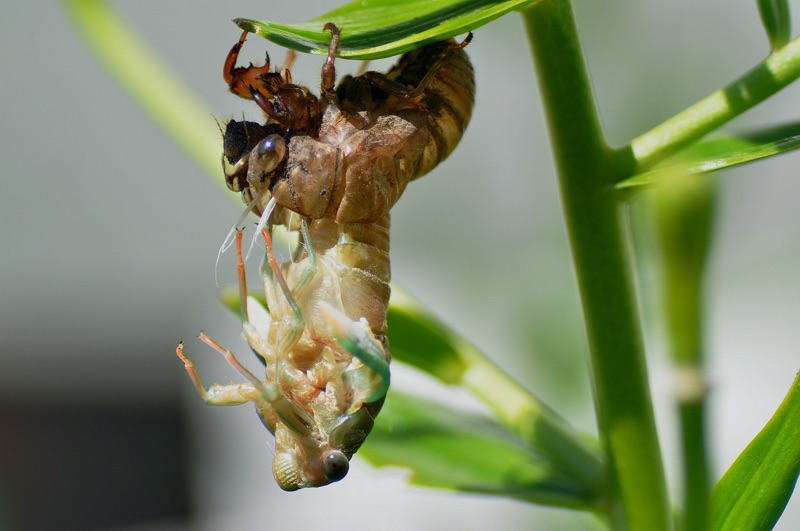
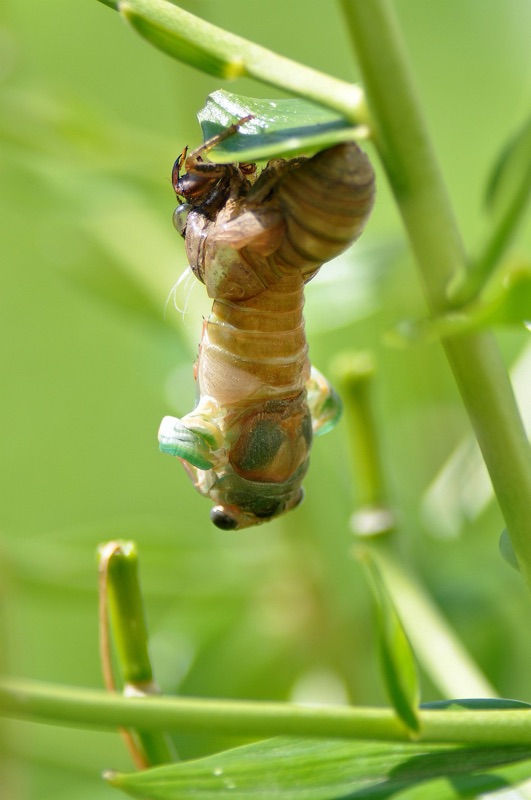
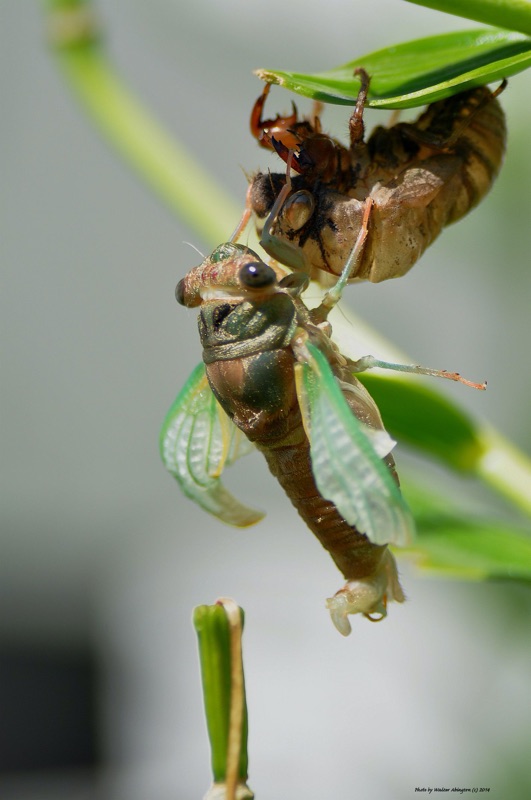
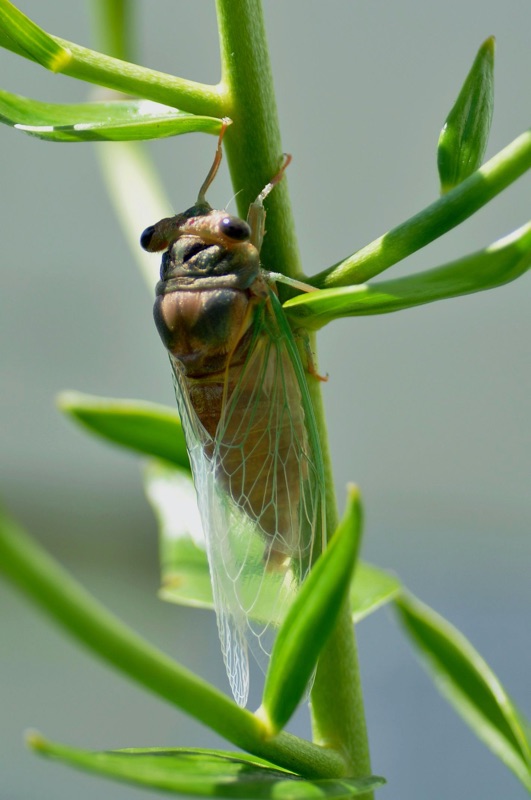
There will be two major periodical cicada emergences in 2015. We’re less that 2 months away!

Brood XXIII, the Lower Mississippi Valley brood:
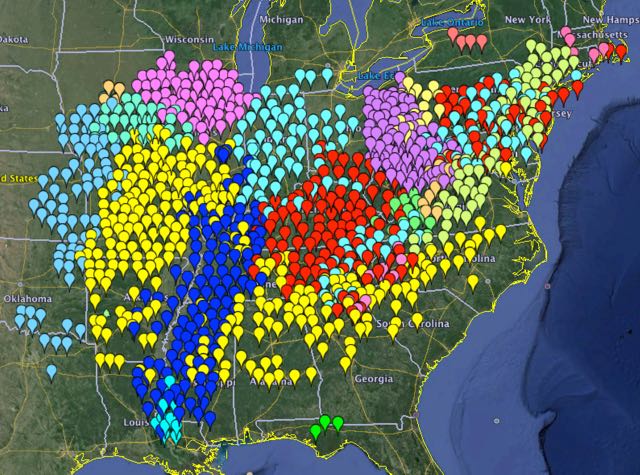
This brood of 13 year Magicicada will emerge in Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas, Tennessee, Missouri, Kentucky, Illinois, and Indiana. Brood XXIII features all four 13 year Magicicada species M. tredecim, M. neotredecim, M. tredecassini and M. tredecula.
When they’ll emerge depends on the weather. A cool spring will mean the emergences will start later in the spring. Regardless of the weather, the emergences will begin in the Southern-most states, sometime in late April or early to mid May.
Brood XXIII should, depending on the weather, start emerging in less than two months; some time in late April in Louisiana.
Brood IV, the Kansan Brood:
This brood of 17 year Magicicada will emerge in Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska, and Iowa. Brood VI features all three 17 year Magicicada species M. septendecim, M. cassini, and M. septendecula.
Brood IV should start emerging in early May.
Brood IV and XXIII won’t emerge in the same year again until the year 2236. The only state that features both Brood XXIII & IV is Missouri, but the areas where they emerge do not overlap.
Stragglers:
The best bet for Stragglers will be Brood VIII (17 year cicadas emerging 4 years early) & XIX (13 year cicadas emerging 4 years late). There is also a chance for III (17yr/1 year late), V (17yr/1 year early), and XXII (13yr/1 year late). Visit our brood page, to see the states where these stragglers might emerge.